Sample collection kitting is an essential component of research and diagnostic workflows that influences the success of subsequent analysis and the reliability of data. However, despite its crucial importance, the process of collecting samples is fraught with challenges that can compromise the integrity of samples, resulting data, and research outcomes. Overcoming sample collection challenges is vital and demands a comprehensive approach to ensuring sample preparation is standardized, optimized, and in line with relevant regulations. Here, we will explore sample collection in more detail, including common challenges and strategies for success.
Table of Contents
The Central Role of Sample Collection Kitting in Research and Diagnostics
Central to the success of any research or diagnostic workflow involving biological samples, the process of sample collection determines the accuracy of results, the reliability of data, and the success of research outcomes or new therapeutic developments. For example, in the realm of drug development, the collection of cell samples is essential for assessing the efficacy and safety of new compounds1. Similarly, in genomic research, the precision in sample collection is directly linked to the accuracy of sequencing and gene expression analyses2, while in diagnostics, the integrity of patient samples is crucial for test sensitivity and specificity3.

Sample Collection Kitting Challenges and Implications
However, despite the critical role of sample collection, researchers encounter numerous obstacles that can significantly affect the integrity of their research and the validity of results4–6.
Common challenges in sample collection kitting include:
- Lack of understanding of the sample and optimal collection methods.
- Inconsistent sampling techniques.
- Sample contamination or damage.
- Loss of sample integrity.
- Limited sample availability.
- Safety issues such as exposure to hazardous materials.
- Time- and labor-intensive protocols which act as a barrier to productivity.
Strategies for Success
Central to overcoming these challenges is gaining an in-depth understanding of the sample and its collection, processing, and storage requirements7. Gaining such knowledge and experience takes time, especially given the high number of diverse sample types often dealt with by a lab. Moreover, precision and consistency are paramount in overcoming these challenges, which require researchers to spend time developing and optimizing standardized protocols if optimal protocols are not available8. It is also essential that any relevant regulations and data protection laws are adhered to9,10, which requires extensive knowledge and a commitment to staying abreast of any changes or updates.
Gaining all of this sample-specific knowledge and experience, as well as developing and optimizing standard protocols for the lab to follow, can be challenging and time-consuming and can negatively impact laboratory productivity. Thus, it can be hugely beneficial to outsource this effort by working with a highly knowledgeable service provider on sample collection.
The Solution: Custom Kitting Services by Sampled
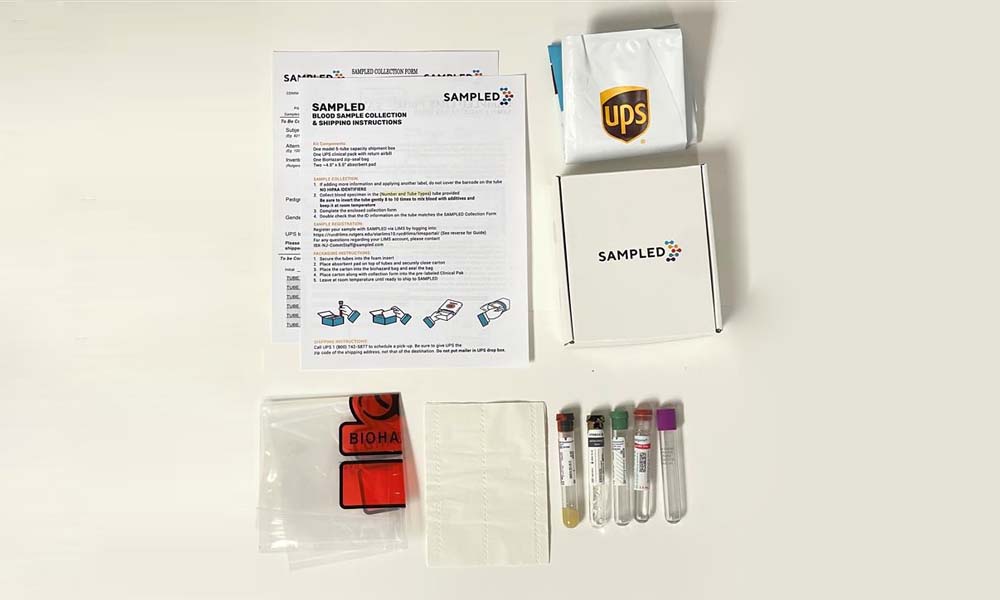
Sampled offers a custom sample collection kitting service designed to streamline the sample collection process for our clients. The kits, tailor-made to meet the client’s needs, are constructed from high-quality materials and are comprehensively quality-checked prior to distribution. Our sample collection kitting services are designed to meet the specific requirements of different sample types, addressing the unique challenges each type presents. Our experts are knowledgeable about sample characteristics and collection methodologies and stay abreast with regulatory changes, which they use to inform the development of our kits, minimizing the risk of sample degradation and contamination and ensuring compliance with regulatory guidelines and data protection laws.
Aside from benefits to sample integrity and resulting data reliability, utilizing Sampled’s custom kitting service can be hugely beneficial for improving laboratory efficiency and productivity. All our sample collection kits come with a single page of simple, easy-to-follow instructions for workflows that are as streamlined as possible. Protocols always follow best practices and are standardized, minimizing variability and maximizing reproducibility in sample collection11. Finally, all sample collection components are barcoded, which streamlines the sample’s transportation, processing, storage, and access, and enables a full chain of custody throughout the sample’s lifecycle.
Conclusion
The significance of successful sample collection in the integrity and reliability of data resulting from analytical workflows cannot be overstated. Challenges inherent to the sample collection process, often stemming from an insufficient understanding of sample requirements or non-standardized protocols, can severely impede the success of these workflows. Sampled offers a custom sample collection kitting service that presents a robust solution to these challenges. Through extensive knowledge and expertise in sample characteristics and collection methodologies, the development of bespoke sample collection kits not only streamlines the collection process but also enhances sample integrity and compliance with regulatory standards, thereby elevating the quality and reliability of research and diagnostic pipelines.
Download the full whitepaper today to learn more about the importance of standardized sample collection procedures and how custom kitting services can help you elevate your sample collection and improve resulting data.
1. Maass KF, Barfield MD, Ito M, et al. Leveraging patient‐centric sampling for clinical drug development and decentralized clinical trials: Promise to reality. Clin Transl Sci. 2022;15(12):2785-2795. doi:10.1111/cts.13411
2. Szczepek AJ, Frejo L, Vona B, et al. Recommendations on Collecting and Storing Samples for Genetic Studies in Hearing and Tinnitus Research. Ear Hear. 2019;40(2):219-226. doi:10.1097/AUD.0000000000000614
3. Nichols ZE, Geddes CD. Sample Preparation and Diagnostic Methods for a Variety of Settings: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules. 2021;26(18):5666. doi:10.3390/molecules26185666
4. Logie JJ, Chaloner C. A national survey of specimen contamination in the UK. Ann Clin Biochem Int J Lab Med. 2019;56(2):219-227. doi:10.1177/0004563218812500
5. Vester AE, Christensen EF, Andersen SK, Tønnesen E. Ethical and practical problems in blood sampling for research purposes during pre‐hospital emergencies. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005;49(10):1540-1543. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2005.00789.x
6. Santos J, Ramos C, Vaz-Velho M, Vasconcelos Pinto M. Occupational Exposure to Biological Agents. In: Arezes PM, Boring RL, eds. Advances in Safety Management and Human Performance. Vol 1204. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. Springer International Publishing; 2020:61-67. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-50946-0_9
7. Redrup MJ, Igarashi H, Schaefgen J, et al. Sample Management: Recommendation for Best Practices and Harmonization from the Global Bioanalysis Consortium Harmonization Team. AAPS J. 2016;18(2):290-293. doi:10.1208/s12248-016-9869-2
8. Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Vieira DN, Magalhães T. Guidelines for Collection of Biological Samples for Clinical and Forensic Toxicological Analysis. Forensic Sci Res. 2016;1(1):42-51. doi:10.1080/20961790.2016.1271098
9. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) | CDC. Published June 28, 2022. Accessed March 4, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/phlp/publications/topic/hipaa.html
10. UCL. Transporting Infectious and Biological Material. Safety Services. Published August 3, 2020. Accessed March 20, 2024. https://www.ucl.ac.uk/safety-services/policies/2022/dec/transporting-infectious-and-biological-material
11. ISBER. Best Practices: Recommendations for Repositories Fifth Edition. Published online 2023. Accessed January 29, 2024. https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.isber.org/resource/resmgr/best_practices/ISBERBestPractices-5thEditio.pdf

